Table of Contents
- Creating an Effective Troubleshooting Plan for Passive Interfaces
- Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Troubleshooting Passive Interfaces
- Utilizing Advanced Techniques to Resolve Issues with Passive Interfaces
- Tips and Tricks for Quickly Resolving Issues with Passive Interfaces
Troubleshooting passive network interfaces can be a challenging task as they are often complex and have a wide variety of configurations. Passive interfaces are typically used in high-performance networks and are designed to provide high-speed and reliable connections. As such, it is important to understand the basics of troubleshooting passive interfaces in order to effectively diagnose and resolve any issues that may arise. This guide will provide an overview of the process of troubleshooting passive interfaces, including common issues that can occur and how to identify and address them.
A Comprehensive Guide to Troubleshooting Passive Interfaces
Passive interfaces are a common component of many network systems today. While they are generally reliable, there are times when they can be troublesome. This guide is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of common issues with passive interfaces and how to troubleshoot them.
1. Check Connections The first step in troubleshooting passive interfaces is to check the connections. Make sure that all cables are securely connected and not loose or frayed. Ensure that the cable type matches the interface type. Also check that the correct port is being used for each connection.
2. Inspect Interfaces Once the connections have been checked, the interfaces themselves should be inspected. Look for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks or chips in the connectors. Make sure that all ports are enabled and configured correctly.
Check Cables
If the connections and interfaces appear to be in good condition, the next step is to check the cables. Make sure that there are no kinks or breaks in the cable. Also check for any signs of corrosion or damage.
4. Re-test Connections If the connections and cables appear to be in good condition, the next step is to re-test the connections. First, make sure that the correct cable type is being used for each connection. Then, test each connection one by one.
5. Check Configuration If the connections are still not working, the next step is to check the configuration. Make sure that the interface is properly configured and that all settings are correct. Check for any software or firmware updates that may be necessary.
6. Replace Interface If all else fails, the last step is to replace the interface. This can be done by disconnecting the old interface and connecting a new one. Make sure that the new interface is compatible with the existing system and that all settings are properly configured. In conclusion, troubleshooting passive interfaces can be a complex process. However, by following the steps outlined in this guide, it is possible to identify and correct any issues that may arise.
Creating an Effective Troubleshooting Plan for Passive Interfaces
Creating an effective troubleshooting plan for passive interfaces can help ensure that any issues with the interface are quickly identified and resolved. In this article, we will discuss how to create an effective troubleshooting plan for passive interfaces. First, it is important to understand the basics of passive interfaces. Passive interfaces are devices that do not actively transmit data, such as modems, switches, and routers. These devices are used to connect two or more networks, allowing for communication between them. Once you have a basic understanding of passive interfaces, the next step is to create a troubleshooting plan. The plan should include a series of steps to help diagnose and resolve problems with passive interfaces. These steps should include:
Steps to Follow
1. Identifying the source of the problem: Determine the source of the issue by looking at the logs, examining the network traffic, and analyzing the system’s performance.
2. Testing the interface: Test the interface to make sure it is functioning correctly. This can be done by running a few simple tests such as a ping or traceroute.
3. Checking for errors: Check the logs for any errors related to the interface.
4. Isolating the issue: Once the source of the problem has been identified, it is important to isolate it from the rest of the network to prevent further issues.
5. Troubleshooting the issue: Once the issue has been isolated, it is time to troubleshoot it. This should include checking the configuration settings, ensuring that the cables are properly connected, and testing the interface to make sure it is functioning correctly.
6. Resolving the issue: The last step is to resolve the issue. This should include fixing any configuration settings, replacing any faulty hardware, and making any necessary changes to the network. Creating an effective troubleshooting plan for passive interfaces is an important part of maintaining a healthy network. By following these steps, any issues with the interface can be quickly identified and resolved.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Troubleshooting Passive Interfaces
When troubleshooting passive interfaces, it is important to avoid common pitfalls that can lead to inaccurate diagnosis and wasted time. Here are some of the most common pitfalls to avoid when troubleshooting passive interfaces:
1. Not checking the physical connection: Before beginning any troubleshooting, it is essential to ensure that the physical connection between the passive-interface and the active device is secure. This includes verifying that the cables are correctly connected and that the passive-interface is properly powered.
2. Not verifying the power supply: It is critical to ensure that the power supply is properly connected and that it is providing a stable and sufficient power supply. If the power is not functioning correctly or is not providing sufficient power, the passive-interface will not be able to operate as intended.
3. Not checking the software configuration: Software configuration issues can often be the cause of problems with a passive interface. It is important to verify that the software configuration is correct and that all settings are properly applied.
4. Not using proper troubleshooting techniques: When troubleshooting passive interfaces, it is important to use the proper troubleshooting techniques. This includes isolating the problem to determine the root cause, narrowing down the possible causes, and then testing each potential cause one by one until the problem is identified and resolved. By avoiding these pitfalls, troubleshooting passive interfaces can be a much more efficient and effective process.
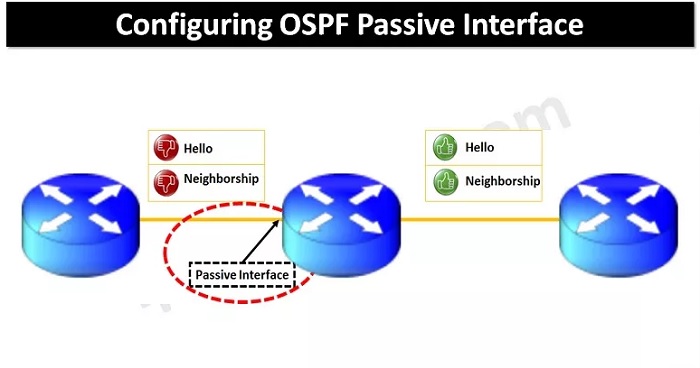
Utilizing Advanced Techniques to Resolve Issues with Passive Interfaces
Passive interfaces are a type of communication interface that does not require external power, and they are often used in a variety of applications, such as industrial automation and smart home systems. While these interfaces are generally reliable, there may be times when they fail to perform as expected. In such cases, advanced techniques can be used to identify and resolve the issue. One of the most effective methods for troubleshooting passive interfaces is to use a protocol analyzer. This device allows you to monitor and analyze the data traffic that is passing through the interface, which can help to identify any potential problems. By analyzing the data frames and packets, you can pinpoint the source of the issue and determine the best course of action.
Passive Interfaces is Oscilloscope Testing
Another technique that can be used to diagnose issues with passive interfaces is oscilloscope testing. This method involves connecting an oscilloscope to the interface and monitoring the voltage levels. If the voltage levels are not within an acceptable range, then this could indicate a problem with the interface. By adjusting the voltage levels, it may be possible to resolve the issue. Finally, a multimeter can also be used to test the passive interface. This device can measure the current and voltage levels of the interface, which can help to identify any issues that may be present.
By making adjustments to the current and voltage levels, it may be possible to resolve the issue with the passive interface. In conclusion, passive interfaces can be difficult to troubleshoot, but utilizing advanced techniques can help to identify and resolve any potential issues. Protocol analyzers, oscilloscope testing, and multimeter testing are all effective methods that can be used to diagnose problems with passive interfaces. With the right tools and knowledge, it is possible to successfully diagnose and resolve any issues that may be present.
Tips and Tricks for Quickly Resolving Issues with Passive Interfaces
1. Check the physical interface connection: Make sure that the cable is securely plugged in and that the physical interface is enabled and operational.
2. Check the interface state: Make sure that the interface is in an up/down state. If the state is down, try resetting the interface.
3. Check the configuration of the interface: Make sure that the configuration is correct and that there are no misconfigurations.
4. Check the routing table: Make sure that the routes for the passive-interface are correctly configured.
5. Check the status of neighboring interfaces: Make sure that the neighboring interfaces are operational and that they are correctly configured.
6. Check the status of the router: Make sure that the router is operational and that it is not experiencing any issues.
7. Check the status of the network infrastructure: Make sure that the underlying network infrastructure is operational and that it is not experiencing any issues.
8. Check for any known issues: Check for any known issues that might be related to the passive interface.
9. Check for any recent changes: Make sure that there have been no recent changes to the network configuration that could be causing the issue.
10. Contact your support team: If all else fails, contact your support team to help you diagnose and resolve the issue with the passive interface.
Final Thought!
Troubleshooting passive interfaces can be a challenging task, but it can be done with the right tools and knowledge. By using basic troubleshooting techniques such as checking the configuration, verifying the physical connections, testing the link status, and using diagnostic tools, you can quickly identify and address the issues causing the interface to fail. With the right approach, you can quickly identify and resolve any issues in the network and get your passive interfaces back up and running.
Comments (0)