Table of Contents
- How Do Frontotemporal Disorders Affect Cognition?
- What are the Common Symptoms of Frontotemporal Disorders?
- What Treatment Options are Available for Frontotemporal Disorders?
- What Genetic Factors Play a Role in Frontotemporal Disorders?
- How Does Diagnosing Frontotemporal Disorders Differ from Other Neurodegenerative Disorders?
How Do Frontotemporal Disorders Affect Cognition?
Frontotemporal disorders, also known as frontotemporal dementia (FTD), are a group of conditions that affect the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. These areas are responsible for a range of cognitive functions, including language, behavior, and decision-making. Consequently, FTD can cause a range of cognitive deficits. Common cognitive deficits associated with FTD include difficulty with abstract thinking, problem-solving, and executive functioning. These deficits can lead to difficulty in planning, organizing, and completing tasks. Additionally, memory problems are common, as is difficulty with language, including difficulty with finding words, understanding conversation, and producing meaningful speech. Behavioral changes are also associated with FTD. People may become more socially inappropriate and may have difficulty controlling their emotions and impulses. They may also exhibit disinhibited behaviors, such as making inappropriate comments or gestures. FTD can also cause changes in personality, including apathy, loss of empathy and compassion, and difficulty with social relationships. Additionally, people with FTD may become more impulsive and exhibit mood swings. The cognitive and behavioral changes associated with FTD can have a significant impact on a person’s life. It can lead to difficulties in maintaining relationships, difficulty at work, and even an inability to live independently. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of FTD, it is important to seek medical advice.What are the Common Symptoms of Frontotemporal Disorders?
Frontotemporal disorders, including frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and primary progressive aphasia (PPA), are a group of neurological conditions that cause progressive decline in language, behavior, and/or movement. Common symptoms of frontotemporal disorders vary depending on the type of disorder, but may include changes in personality, language deficits, difficulty with multitasking, and motor difficulties. Personality changes are often seen in individuals with FTD. Affected individuals may become socially inappropriate, uninterested in activities they previously enjoyed, or display changes in their decision-making or behavior. Language deficits, such as difficulty understanding language or speaking, are common in those with PPA. Difficulty multitasking and problems with executive functioning, such as organizing, planning, and problem-solving, are also common in frontotemporal disorders. Finally, motor difficulties, including difficulty walking and writing, can also be seen. It is important to note that the symptoms of frontotemporal disorders can vary significantly from person to person and can also change over time. If you are concerned that you or a loved one may be experiencing these symptoms, it is important to speak to a medical professional.What Treatment Options are Available for Frontotemporal Disorders?
Frontotemporal disorders (FTDs) are a group of disorders that affect the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, which are responsible for regulating behavior, emotion, language, and other aspects of cognition. Treatment options for FTDs vary depending on the specific disorder, the severity of symptoms, and other factors. Medication is one of the most common treatment options for FTDs. Commonly prescribed medications include antidepressants, antipsychotics, and cholinesterase inhibitors, which can help to reduce symptoms such as agitation and impulsivity. Additionally, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) may be prescribed to help manage depression and anxiety. Psychotherapy is another treatment option for FTDs. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can help to modify behaviors and improve communication skills, while family therapy can help to educate family members about the disorder and provide support. Additionally, support groups can help to connect individuals with similar conditions and provide a sense of community. In some cases, lifestyle changes may be recommended to help manage symptoms. These can include dietary changes, exercise, and stress management techniques. Additionally, occupational therapy may be recommended to help individuals maintain or improve their ability to perform daily activities. Finally, in some cases, surgery may be an option for FTDs. The most common type of surgery is a frontal lobotomy, which is used to reduce agitation and aggression. Other types of surgery may be recommended depending on the specific disorder and the severity of symptoms. In summary, treatment options for FTDs vary depending on the individual and the specific disorder. Medications, psychotherapy, lifestyle changes, and surgery are all potential treatment options. It is important to work with a medical professional to determine the best treatment plan for your individual needs.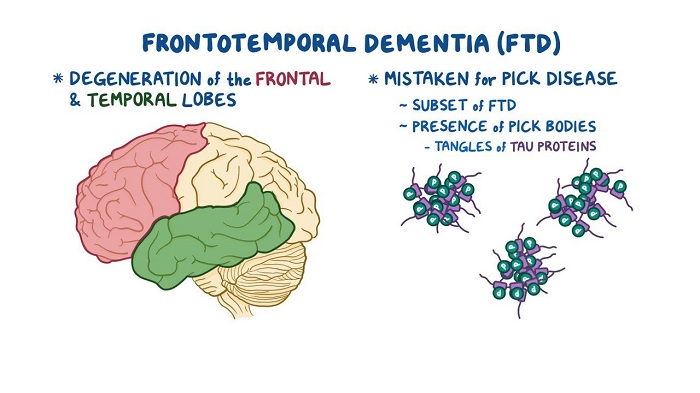
Comments (0)