Table of Contents
- An Overview of What a Hypervisor Is and How It Functions
- Different Types of Hypervisors: The Pros and Cons of Each
- How to Choose the Right Hypervisor for Your Business
- Understanding the Benefits of Using a Hypervisor for Virtualization
- Best Practices for Deploying and Managing a Hypervisor Environment
An Overview of What a Hypervisor Is and How It Functions
A hypervisor is a type of virtualization technology that allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical computer system. It is a layer of software that sits between the physical computer system and the operating systems of the virtual machines, allowing the virtual machines to share the resources of the physical system. In order to understand how a hypervisor works, it is important to understand the concept of virtualization. Virtualization is the process of creating and running virtual machines on a single physical computer. Each virtual machine is an isolated environment in which a different operating system can be installed. The hypervisor is the software component responsible for managing the resources of the physical system and the virtual machines. It is responsible for providing the virtual machines with access to the physical system’s resources, such as memory, storage, and networking. It also ensures that the virtual machines do not interfere with each other’s operations. When a user requests a VM, the hypervisor allocates the resources of the physical system to the VM. The hypervisor also manages the VMs’ memory and storage, and ensures that the VMs have access to the networking resources. The hypervisor is also responsible for monitoring the performance of the VMs and the physical system. It can adjust the allocation of resources as needed to ensure that the VMs are running efficiently and that the system is not overburdened. In short, a hypervisor is a layer of software that sits between the physical computer system and the virtual machines, allowing them to share the resources of the physical system and ensuring efficient performance of the virtual machines.Different Types of Hypervisors: The Pros and Cons of Each
Hypervisors are virtualization software programs that enable the creation of multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical computer or server. They provide the core infrastructure for virtualized environments, allowing for the efficient utilization of hardware resources and the easy deployment of applications across multiple machines. There are several different types of hypervisor available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most commonly used hypervisors are Type 1 (or bare-metal) and Type 2 (or hosted) hypervisors. Type 1 Hypervisor: A Type 1 hypervisor, also known as a bare-metal hypervisor, runs directly on the host hardware and is responsible for managing the hardware resources, including allocating and distributing processor time, memory, storage, and other resources. This type of hypervisor is designed to be lightweight and efficient because it does not have to run a separate operating system (OS). Pros: High performance: Since the hypervisor runs directly on the hardware, there is less overhead involved and the performance of the virtual machines (VMs) is usually higher than when using a Type 2 hypervisor. • Security: The hardware is isolated from the VMs, which helps to improve the security of the environment. • Flexibility: Type 1 hypervisors can be easily configured to support different types of VMs and can be easily modified to support new technologies. Cons: Expensive: Type 1 hypervisors typically require dedicated hardware, which can be expensive. • Complex setup: Setting up and managing a Type 1 hypervisor can be more complex than using a Type 2 hypervisor. Type 2 Hypervisor: A Type 2 hypervisor, also known as a hosted hypervisor, runs on top of an existing operating system (OS). It is responsible for managing the hardware resources and creating virtual machines (VMs). Pros: Cost-effective: Type 2 hypervisors are typically cheaper than Type 1 hypervisors because they do not require dedicated hardware. • Easy setup: Setting up and managing a Type 2 hypervisor is usually easier than a Type 1 hypervisor, as the host OS is already installed and configured. • Flexible: Type 2 hypervisors can be easily configured to support different types of VMs. Cons: Lower performance: Since the hypervisor has to run on top of an existing OS, it can affect the performance of the VMs. • Vulnerability: The VMs are not isolated from the host OS, which can lead to security vulnerabilities. In conclusion, the type of hypervisor you choose will depend on your specific requirements. Type 1 hypervisors are typically more powerful and secure, but can also be more expensive and complex to setup and manage. Type 2 hypervisors are cheaper and easier to manage, but can have lower performance and be vulnerable to security threats.How to Choose the Right Hypervisor for Your Business
Choosing the right hypervisor for your business is an important decision that can have significant impact on the success of your organization. It is essential to consider the needs of your business, the available resources, and the cost of the hypervisor you are choosing before making a final decision. First, consider the type of workloads your business requires and the type of environment you need to support them. For example, if you are running a web server or database, you may need a hypervisor that offers higher performance than one designed for a simple task such as running a virtual desktop. Second, consider your budget. Hypervisors come in a variety of price ranges and, depending on the features and capabilities you need, the price can vary significantly. Be sure to consider the upfront costs as well as any ongoing costs associated with maintaining and operating the hypervisor. Third, consider the available resources. Different hypervisors require different amounts of resources, such as memory, disk space, and CPU power. Be sure to choose a hypervisor that can run efficiently on the resources you have available. Finally, consider the support options offered by the hypervisor. Be sure to choose a hypervisor that can provide the level of support you need, including technical support and updates. By taking the time to consider the needs of your business, the available resources, and the cost of the hypervisor you are choosing, you can ensure that you select the right hypervisor for your business.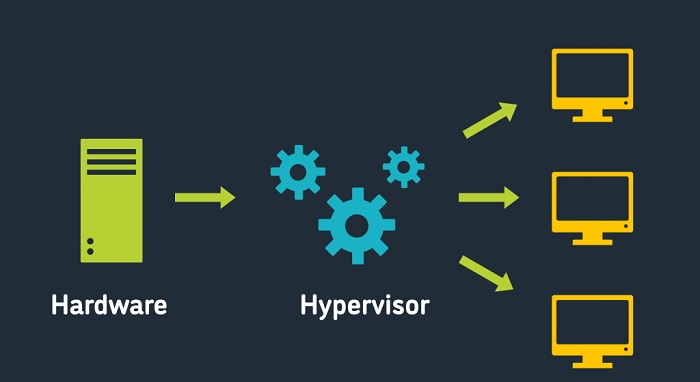
Comments (0)